OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
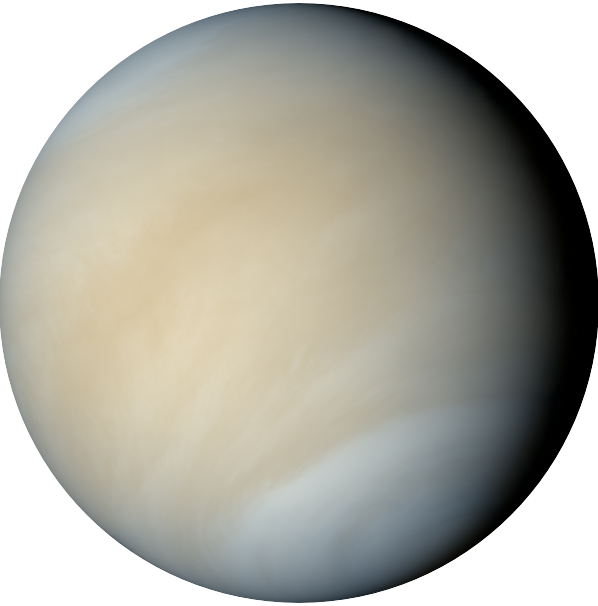

VENUS
EARTH
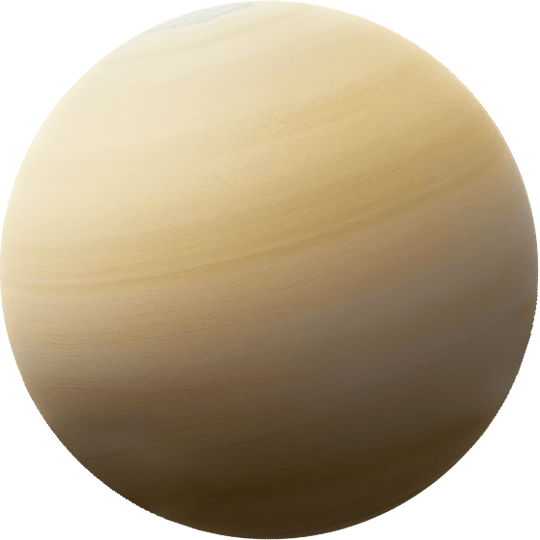

SATURN
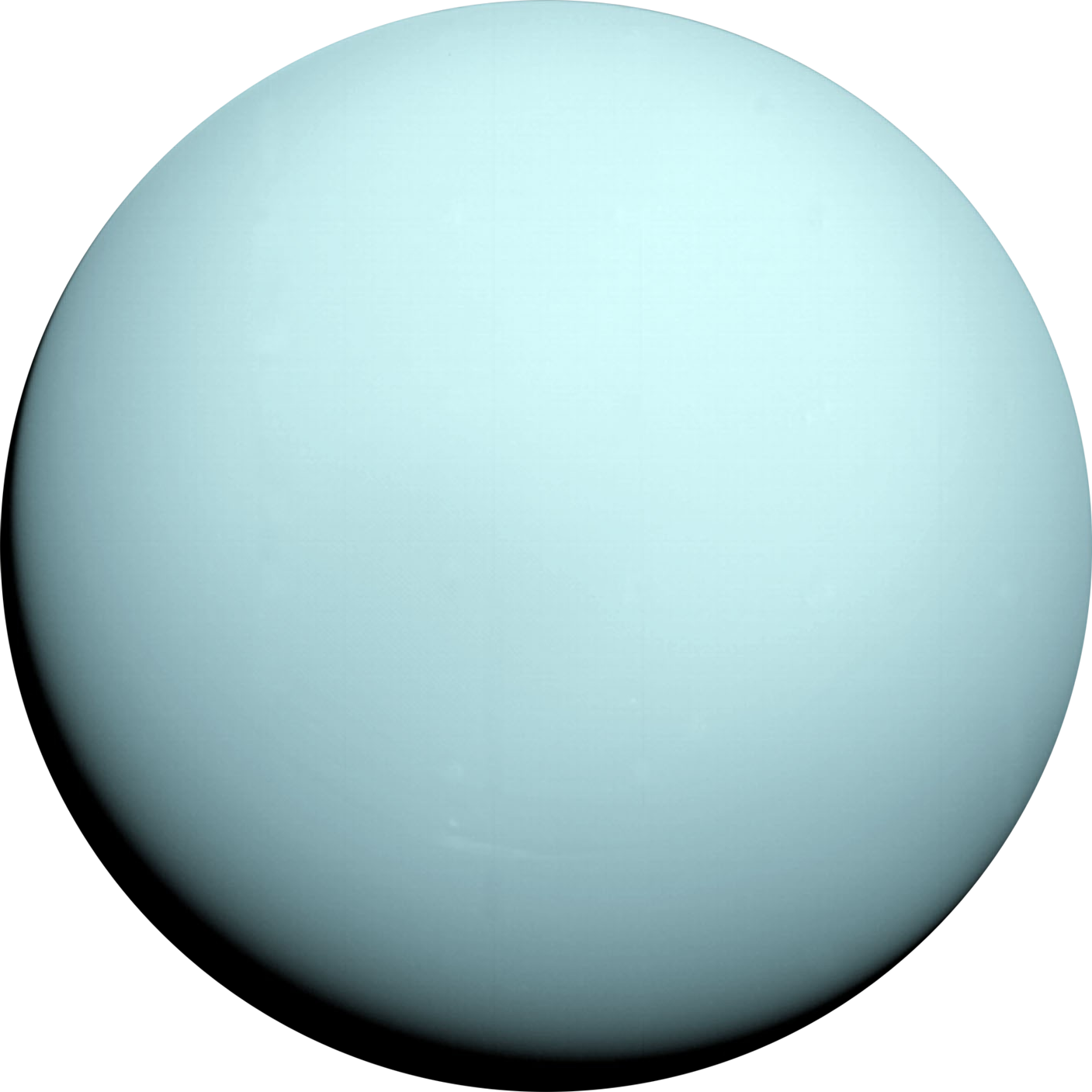

URANUS
Featured news
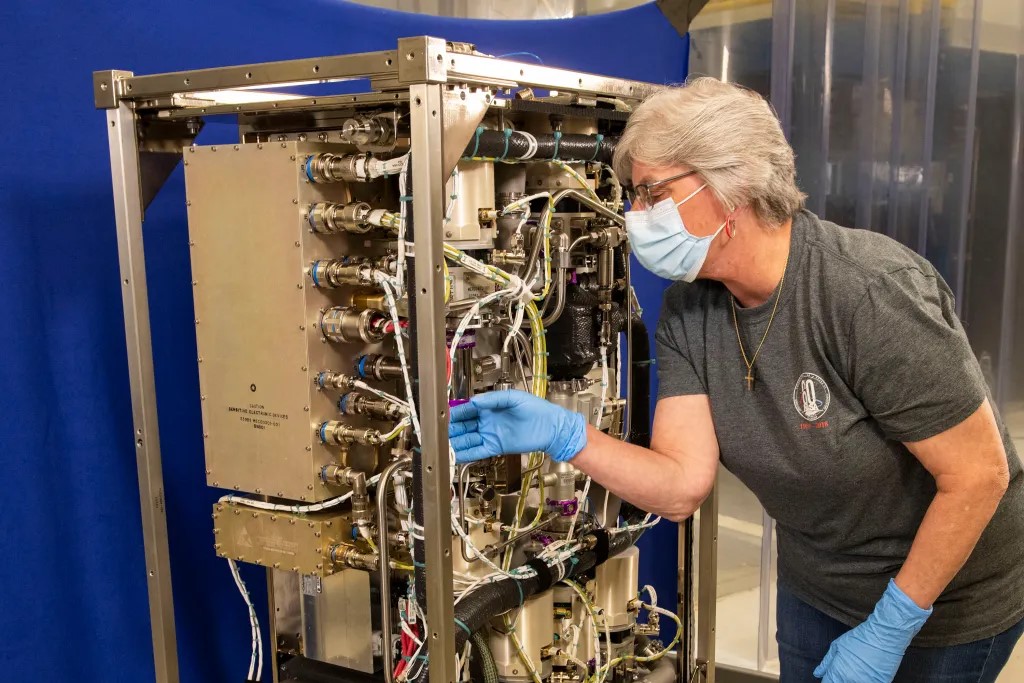
NASA Invests in Artemis Studies to Support Long-Term Lunar Exploration

Missions
BE THE ASTRONAUT!
Ever wondered what it’s like to step into an astronaut’s boots? Interact with our 3D astronaut model—rotate, and explore every detail of the suit that protects astronauts in the harshest conditions of space.
Vaš preglednik ne podržava 3D modele. Pokušajte u Google Chrome ili Microsoft Edge.
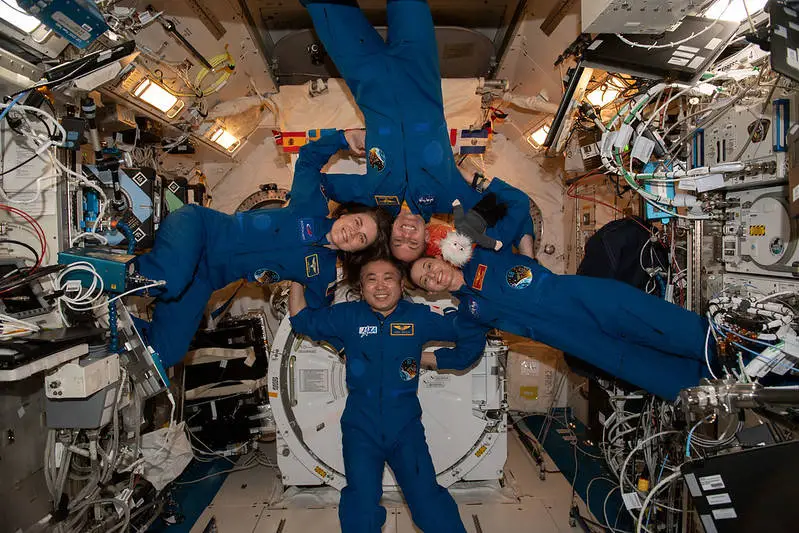
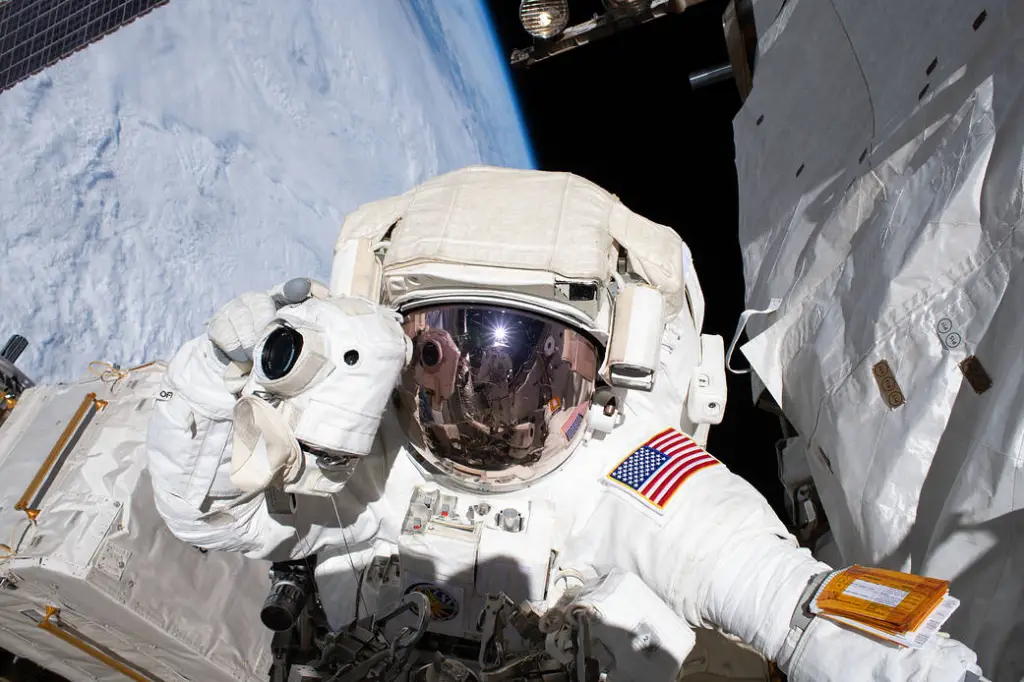
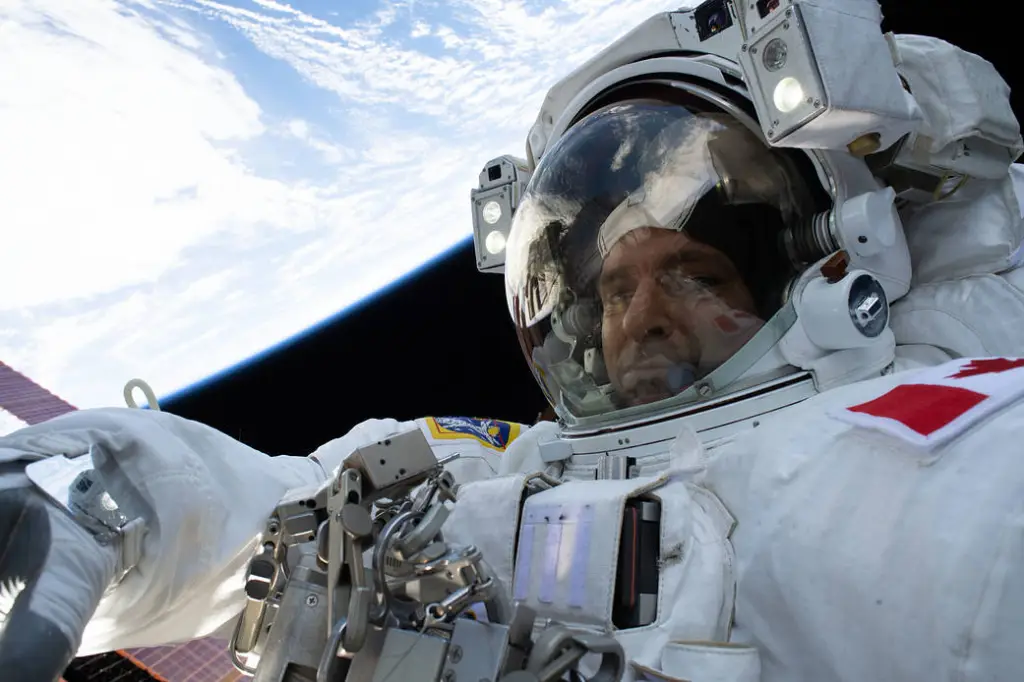
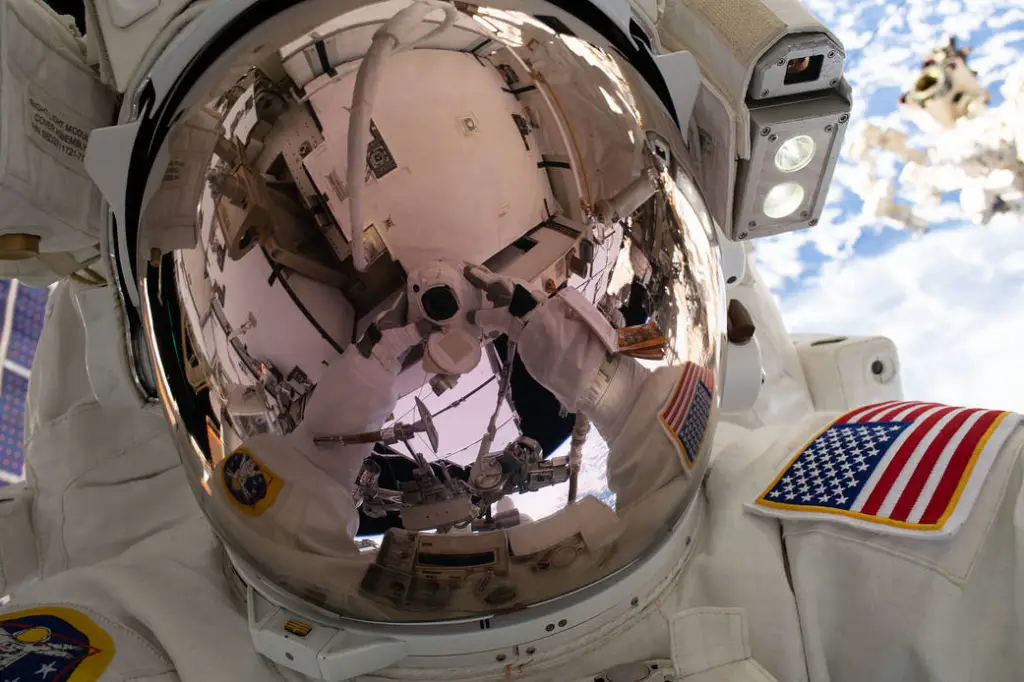
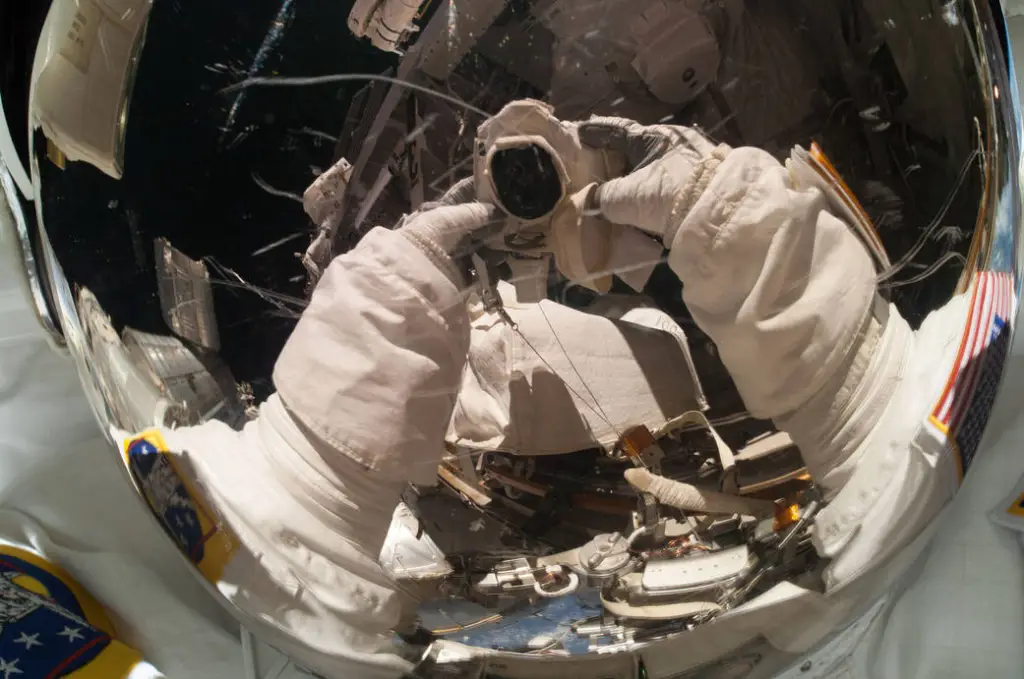
At the space station
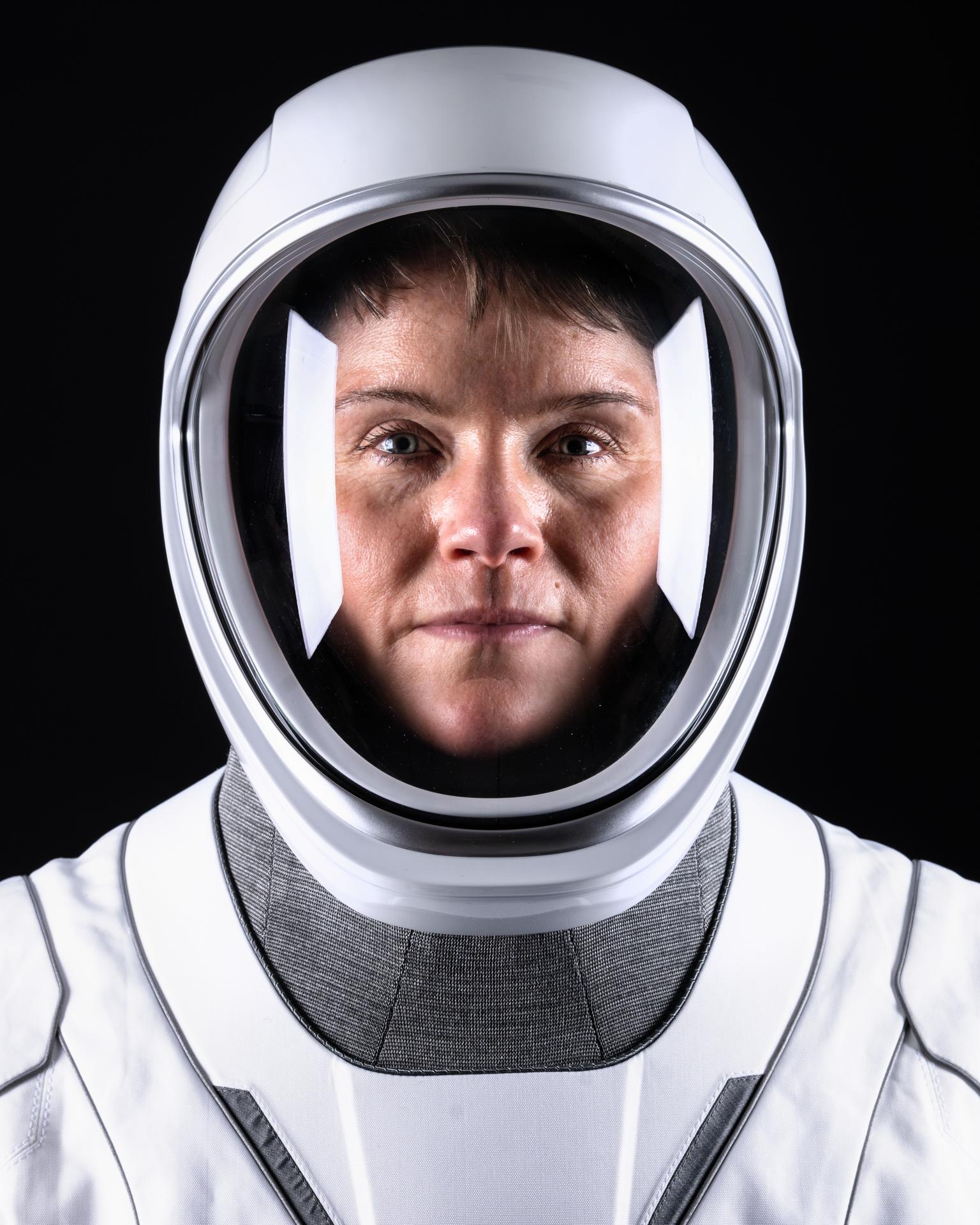

Anne C. McClain
Anne C. McClain was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2013. On her first spaceflight, McClain spent 204 days as a flight engineer during Expeditions. Most recently, McClain launched as commander of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission on March 14, 2025
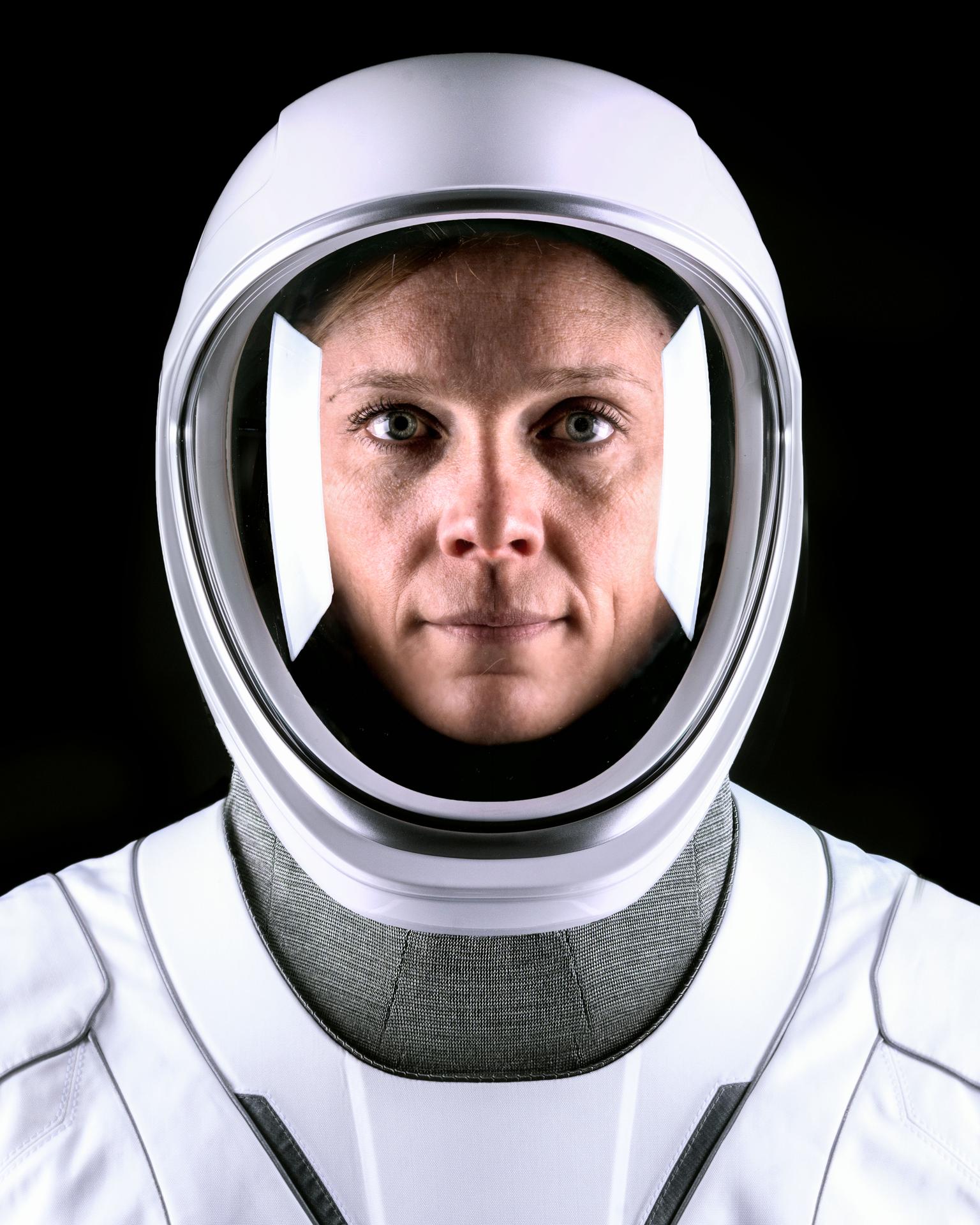

Nichole Ayers
Nichole Ayers was selected as a NASA astronaut in 2021. For her first spaceflight, Ayers launched as pilot of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission on March 14, 2025, to conduct research, technology demonstrations, and the microgravity laboratory.
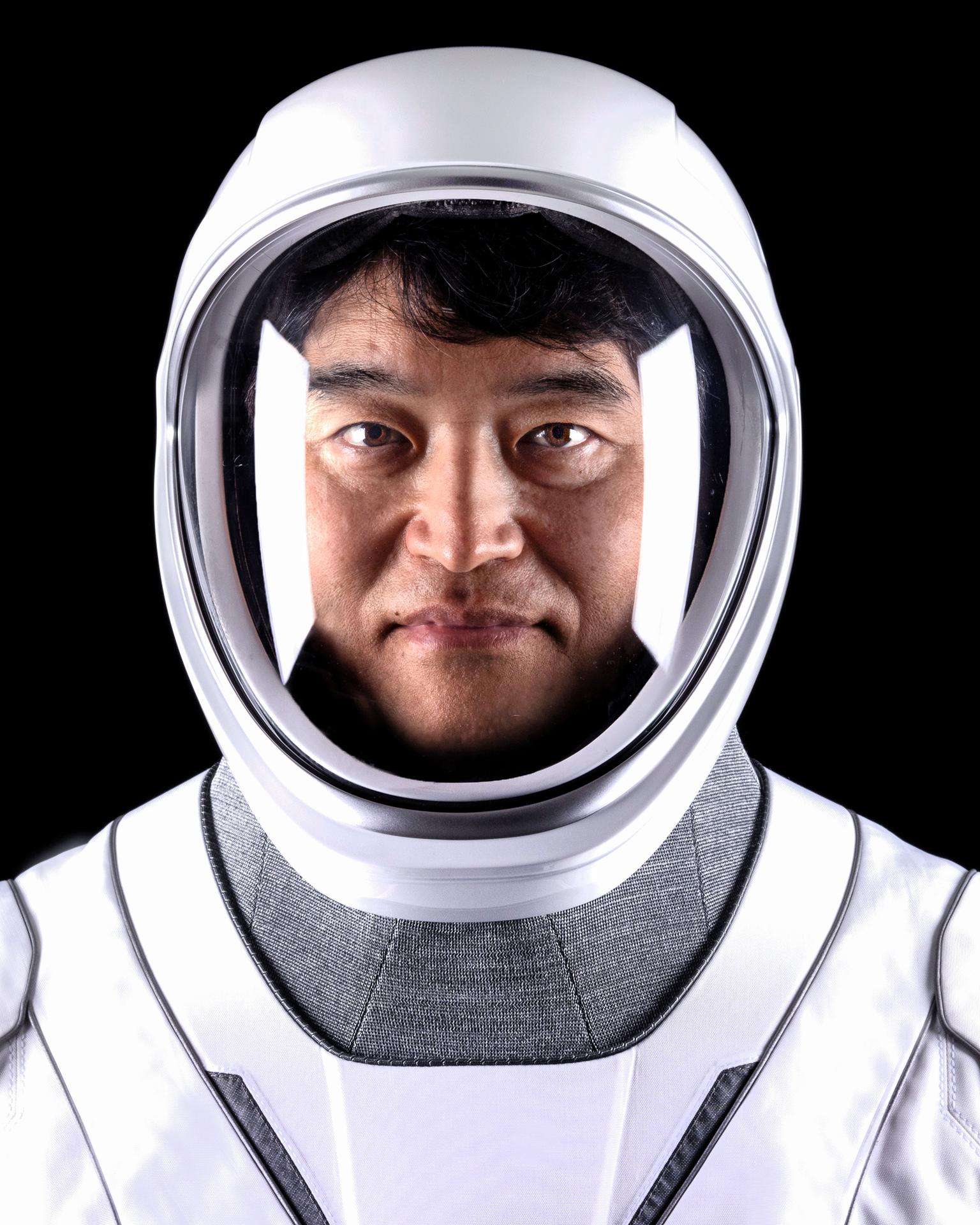

Takuya Onishi
Takuya Onishi is a Japanese astronaut selected for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in 2009. He spent four months on board the International Space Station in 2016. In March 2025, he arrived at the ISS as part of Expedition 72/73.
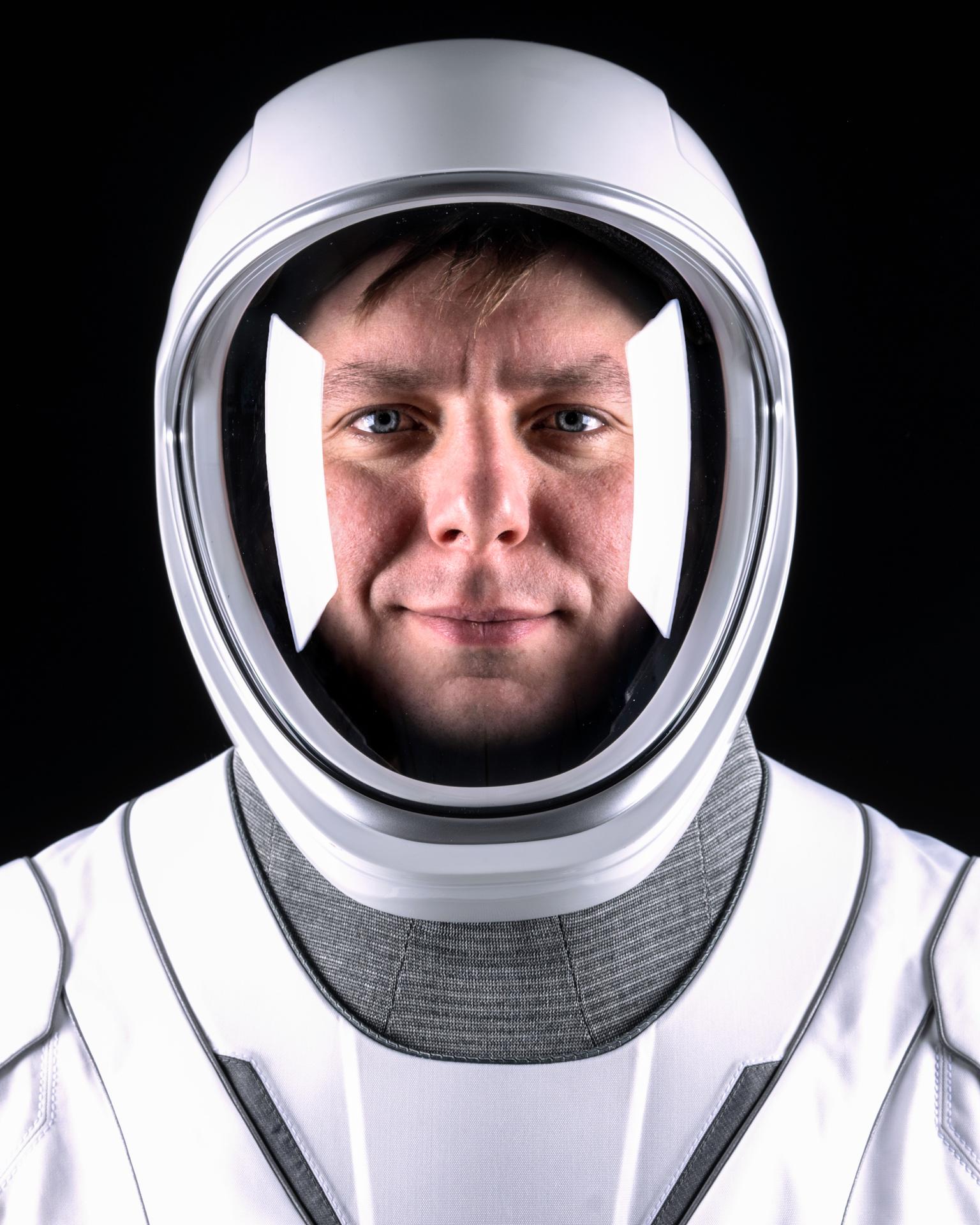

Kirill Peskov
Kirill Alexandrovich Peskov is a Russian cosmonaut who is serving as a flight engineer as part of the long-duration Expedition 72 and 73 missions to the International Space Station flying aboard SpaceX Crew-10.
- 1957 – Sputnik 1: The Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite, marking the beginning of the space age.
- 1961 – Yuri Gagarin: Became the first human to travel into space and orbit the Earth aboard Vostok 1.
- 1969 – Apollo 11: Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the Moon.
- 1998 – ISS: The construction of the International Space Station began, creating a permanent human presence in low Earth orbit.
- 2021 – Inspiration4: SpaceX completed the first all-civilian orbital mission, opening doors for private space travel.
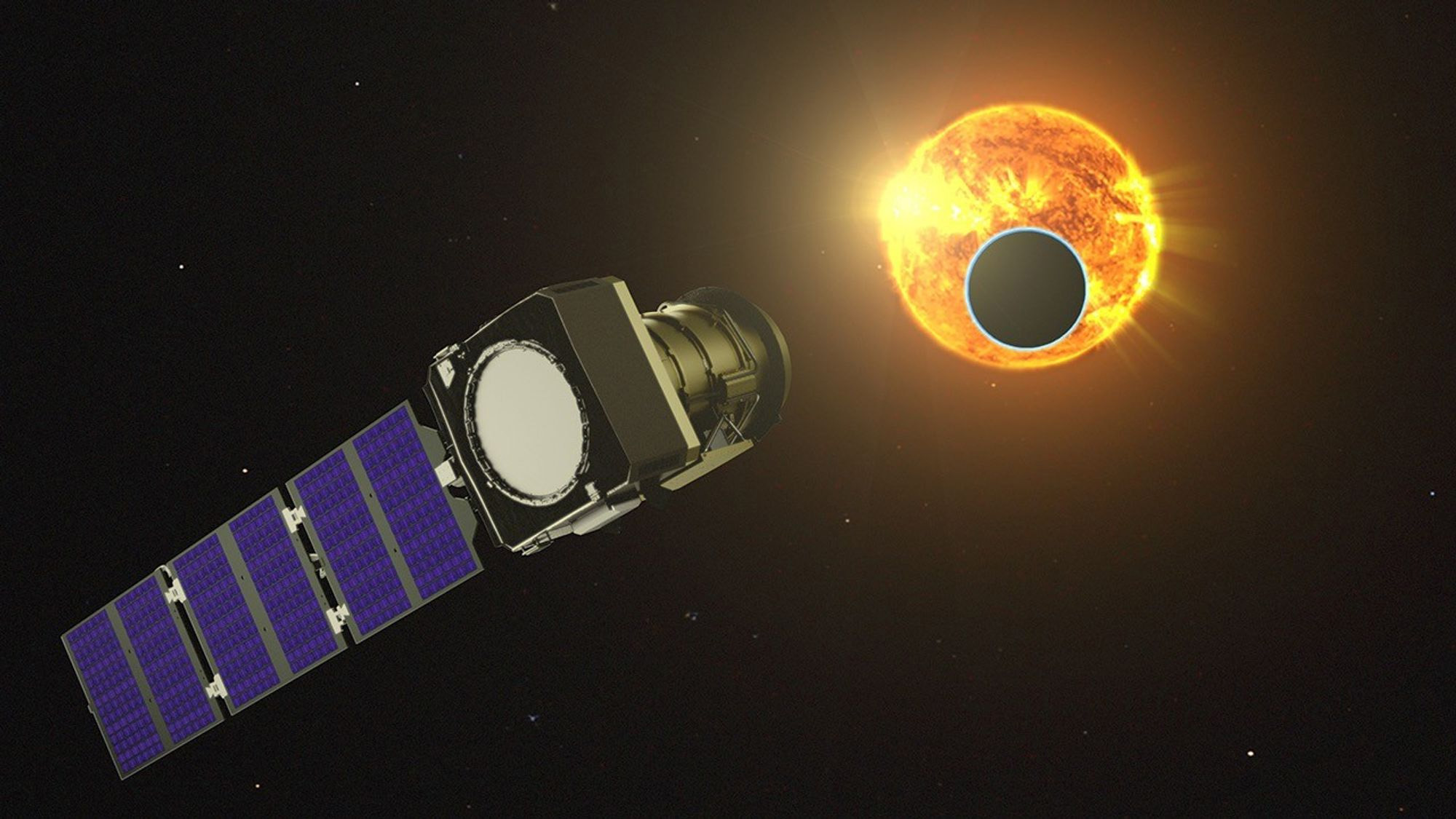
Telescopes collect light and magnify distant objects to help astronomers observe stars, planets, and galaxies far beyond our reach. There are two main types: refracting telescopes, which use lenses, and reflecting telescopes, which use mirrors.
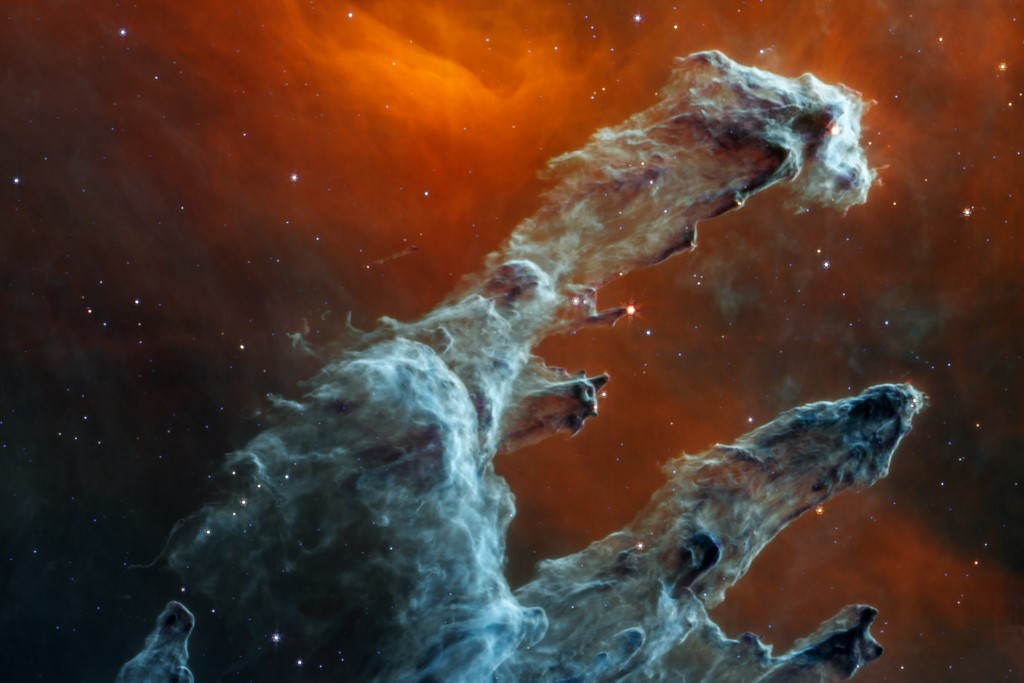
Modern space telescopes, like Hubble and James Webb, operate outside Earth's atmosphere, giving us clearer and more detailed views of the universe. Infrared telescopes like James Webb can even peer through cosmic dust and detect heat emitted by celestial bodies.